

How do I clean my hearing aid?
Wipe the outside of the hearing aid with a cloth or tissue.
If your hearing aid has a wax guard, change this when you notice it is full of wax, or if the hearing aid doesn't work.
Where and how should I keep my hearing aids when I'm not using them?
Keep your hearing aids in a cool dry place when not in use.
Open your battery door when hearing aids are not in your ears to save battery.
What should I do when there is no sound or when the sound is weak or distorted with my hearing aids?
Change the battery. Make sure the battery is not upside down. Make sure battery door is fully closed. Clean opening of hearing aid or earmold. Clean/change the tubing and/or wax guards. If problem persists, make an appointment.
What should I do if my hearing aids make a whistling sound?
Re-insert ear mold or tip and be sure it is inserted correctly. Reducing the volume can also decrease whistling. If problem persists, make an appointment.
How long will my batteries last?
- Size 10 (yellow) = 3 to 5 days
- Size 312 (brown) = 5 to 7 days
- Size 13 (orange) = 10 to 14 days
- Size 675 (blue) = 14 to 21 days
- Rechargeable = charge aids every night
How can I make my hearing aid battery last longer?
Open battery door when not wearing aids. Let battery sit for 1-2 minutes after peeling off the sticker to ensure it is fully activated.
My hearing aid got wet, how should I dry it out?
Remove battery as soon as possible. Place hearing aid in dehumidifier overnight if you have one. Do not try a new battery until hearing aid has dried completely. NEVER use a hair dryer on your hearing aids and NEVER put your hearing aid in the microwave or oven. If hearing aid does not power on or sounds weak, call or text us to make an appointment.
How should my family and friends speak to me now that I use hearing aids?
Others should get your attention before speaking to you.
Others should speak in a normal voice, and not shout.
Others should not communicate from a different room. They should be facing you and in close distance.
Others should avoid noisy backgrounds for communication.
How is hearing loss diagnosed?
If you have symptoms of hearing loss, you should see an audiologists to have your hearing tested. Your hearing test, or audiological evaluation, allows the audiologists to determine the type and degree of your hearing loss. The hearing test will also include a case history and a visual inspection of your ear canal and eardrum. Additional tests may be obtained to determine the status of your middle ear function. The results of your hearing test are plotted onto a graph called an audiogram. The audiogram provides a visual of your hearing results across different frequencies or pitches, particularly the ones that are necessary for speech understanding. Your audiogram is used to create a prescription in which hearing aids can be programmed if necessary.
What are the different degrees of hearing loss?
On the top of an Audiogram, from left to right are the different pitches of frequencies. On the left side are the different levels of volume. Soft sounds are on the top of the graph, and loud sounds are towards the bottom. Your hearing level is measured in decibels and can be described by severity of loss. Many professionals will use the following categories to determine the degree of hearing loss.
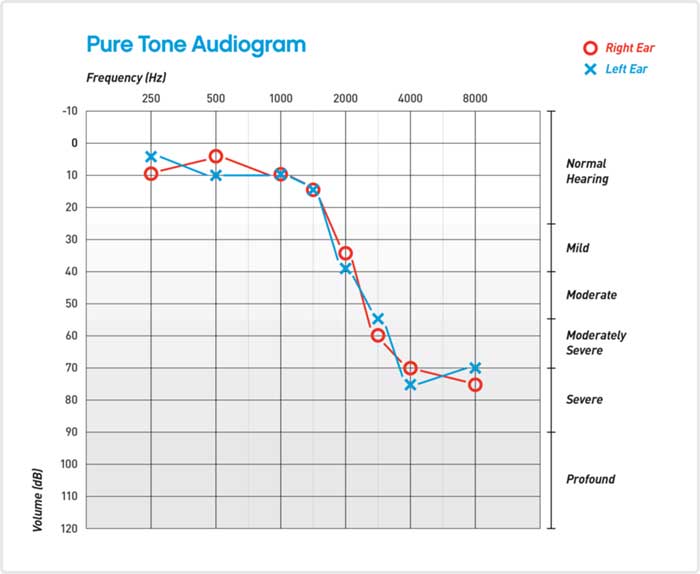
What are the different types of hearing loss?
There are three types of hearing loss.
- Sensorineural hearing loss is when the hearing loss is caused by a problem in the inner ear. This typically occurs from damage to the small hair cells in the auditory system. Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common type of hearing loss. The most common causes of sensorineural hearing loss are age related hearing loss and noise exposure. Treatment for sensorineural hearing loss is hearing aids.
- Conductive hearing loss is when the hearing loss is caused by a problem in the outer or middle ear. Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound cannot be transmitted efficiently through the ear canal, eardrum, or tiny bones in the middle ear. This results in a reduction of the loudness that sound is heard. Conductive hearing loss can result from earwax blocking the ear canal, fluid in the middle ear, middle ear infection, obstruction of the ear canal, a perforation in the eardrum, or any disease of the middle ear bones. Patients with conductive hearing loss can potentially benefit from hearing aids, medication, or surgery.
- Mixed hearing loss is when hearing loss occurs due to problems in the outer/middle and inner ear. Mixed hearing loss involves both sensorineural and conductive hearing loss. Treatment options for mixed hearing loss include hearing aids or surgery, depending on the nature of the impairment and the symptoms that the patient experiences.
What is tinnitus?
Tinnitus is a common disorder that affects over 50,000,000 people in the United States. You may hear it referred to as ringing in the ears, although some people hear other sounds such as hissing, roaring, buzzing, whistling, or clicking. Tinnitus is not a disease, but rather a symptom of another underlying condition of the ear or auditory nerve. Tinnitus can be constant or intermittent, and present as a single tone or multiple tones. Tinnitus is often a side effect of hearing loss. People who suffer from tinnitus as a result of hearing loss, can typically benefit from the use of hearing aids.
What is the difference between an audiologists and a hearing instrument specialist?
Audiologists and hearing instrument specialists are two of the most common professionals that provide treatment for hearing loss. To better understand which professional is best for you, it is important to determine the differences between the two. Audiologists is trained to diagnose, treat, and monitor disorders of the hearing and balance system. Audiologists are trained in anatomy and physiology, amplification devices, acoustics, psychoacoustics, and auditory rehabilitation. Doctors of audiology complete an undergraduate and a doctoral level degree in Audiology, as well as a supervised externship prior to state license sure and national certification. A doctorate degree in audiology requires eight years of post-secondary education. After completing eight years of education, Audiologists must also pass a national standardized exam in order to be eligible for a state license. A hearing instrument specialist is licensed to perform audiometric testing to sell and fit hearing aids. In order to obtain a license, hearing instrument specialists have to take a certification program in hearing aids, complete in the field training hours, and pass an exam. Hearing instrument specials are licensed to fit and repair hearing aids, however they cannot diagnose hearing loss.
Do hearing aids use special batteries
The majority of hearing aids today use zinc-air batteries. This kind of battery is made specifically for hearing aids and it comes in a variety of sizes. You can find hearing aid batteries at almost any store that sells regular batteries, including pharmacies and grocery stores. The length of a hearing aid battery depends on the size of the battery, and how many hours a day you were hearing aid. Another factor is how severe ones hearing loss is. A smaller hearing aid battery will need to be replaced more often while a larger hearing aid battery can last up to 2 to 3 weeks.
I have hearing loss in both ears, is it necessary to wear two hearing aids?
Two hearing aids are better than one hearing aid for several reasons. When wearing two hearing aids you will hear better in a noisy environment, and your ability to localize sound is increased. By using information from both sides of the head our brain can process speech signals more efficiently, especially when in noise. Your brain also uses information from both the right and left sides of your head to determine the direction of a sound. Having only one hearing aid can alter your sense of direction, often making people feel unbalanced.
What style of hearing aid should I wear?
Your audiologists or hearing instrument specialist can help you make an appropriate choice based on your degree of hearing loss, the shape of your outer ear, the size and shape of the ear canal, and your personal preferences.
What brand of hearing aids should I choose?
Most audiology practices work with a variety of hearing aid manufacturers. We at Waterville audiology support all hearing aid manufacturers. This is a discussion that you should have with your audiologists or hearing instrument specialist.

Will a hearing aid restore my hearing to normal?
No. A hearing aid is not designed to make your hearing normal. A hearing aid is designed to make things easier to hear, but it cannot restore the natural function of your ear.
How long will my hearing aid last and how often does it need to be replaced?
Hearing aids are tiny computer chips that are worn on your ears every single day. They work very hard to help you hear. The lifetime of a hearing aid is between four and six years. Four years is when the manufacturers develop new hearing aid technology, in which it is beneficial to upgrade. Hearing aids that are over six years old often need to be repaired more often. You should expect to replace your hearing aids every 4 to 6 years.
